The previous articles introduces partition table which is essential to hard drive, and this chapter will represent file system which is equally important.
File system
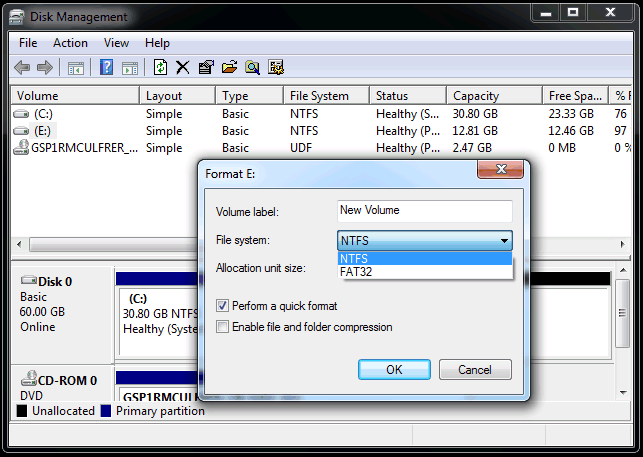
It is known to all that hard drive can be used to store data only after formatting. What is formatting? The previous chapter has explained that newly created partition on hard drive can't be used until data storing format is built. The data storing format can be called file system and formatting is the process of writing file system to partition.
The first thing you should do is please do not save any new data on the formatted hard drive, or it will cause your file overwritten. But don't worry, on the following we will introduce the best formatted hard drove recovery program to help you recover lost files from a formatted hard drive. Why Format Hard Drive. If you own a Windows computer, the hard drive in your system is probably running the NTFS format, which stands for New Technology File System. While the 'New' is originally referring to the year 1993, it has since been improved and updated over the years. Open & View Hard Drive Partitions. NTFS file system viewer extracts items from hard drive and loads them on the software. It retrieves all data like images, audio files, documents, video, powerpoint files, etc., from selected hard disk. The tool displays data in the same manner as the original one. The desktop works fine but the laptop refuses to give me access to files on the WD external hard drive. It says I haven't got authority to access these files. I've tried changing the security settings to 'Everyone' not nothing changes! When I plug the WD into the desktop computer I can access all the files, no problem.
After formatting, partition can be recognized by operating system and used to store and access data.
File system has a variety of formats, and different partitions on a same hard drive can use different file systems. As to Windows system, the most frequently used file system are FAT and NTFS. Next, we'll introduce these file system formats one after another.
RAW
In fact, RAW is not file system format. Generally, RAW partitions are those that can't be recognized by Windows system. RAW partition is either unformatted partition or damaged partition whose file system gets corrupted due to certain reasons. RAW partition usually reports error messages like 'Unformatted' or 'Damaged' under Windows.
RAW partition is not accessible and it can be used after formatting.
Important: If RAW partition contains important files, you need to recover files first before formatting.
FAT
There are three varieties of FAT (File Allocation Table): FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. FAT12 is suitable for very small partitions and it is often used on floppy disks, while FAT16 is used on hard drive volumes whose size ranges from 16MB to 2GB. Thus, FAT12 and FAT16 are rarely used today, and when people say FAT file system they mean FAT32.
As to FAT32 file system, we should know two points: 1. The size of single files should be within 4GB; 2. FAT32 partition is usually less than 32GB, otherwise performance will be affected.
These two limitations make it scarcely used by hard drive which usually produced with volume larger than 1TB. FAT file system is currently widely applied to USB flash drive, memory card, etc.
NTFS
NTFS is the most suitable file system for computer partitions. For the moment, almost all computer runs with NTFS partitions. Compared with FAT, NTFS has a lot of advantages, such as it eliminates those two restrictions of FAT32 mentioned above.
One possible confine of NTFS might be that it is developed by Microsoft and the insider technology has never been officially released. Therefore, your computer will not be able to use NTFS file system once you install other operating system on it, such as Linux.
Windows has small market share in removable products field. Your cell phones, MP5, digital camera, etc. don't run Windows, and storage devices of these products such as USB flash drive, memory card and flash memory don't use NTFS either. Those tiny and portable devices mainly utilizes FAT which can work with removable machines as well as Windows computer.
Another shortcoming of NTFS is that it is initially designed for traditional mechanical hard drives, so NTFS isn't a good choice for storage devices produced on the basis of flash memory (e.g. USB flash drive, SSD, SD card, etc.). That's because NTFS might shorten the lifespan of those removable devices due to NTFS working mechanism. This is why many people don't suggest portable devices opt NTFS file system.
EXFAT
As the capacity of USB flash drive and SD card increases tremendously these days, and FAT32 is no longer efficient enough to manage these devices. To cover the shortage, exFAT was introduced, which eliminated limits of FAT32 practically.
A note about exFAT is that it was also introduced by Microsoft specially for flash memory storage (e.g. USB flash drive, SSD, SD card, etc.) instead of hard drives. EXFAT has been come into use for shorter time and it requires authorization from Microsoft. Besides, many removable machines especially those old machine don't support exFAT.
Advice: with regard to SSD, if it is placed in computer, then please use NTFS file system, and make the SSD 4K sectored aligned which will be explained later; if SSD is used as external hard drive, then exFAT is the best option.
Format Hdd Win 10
View partition file system through DiskGenius
We've discussed so much about file system theoretically, now let's have a look at partition file system:
It has been mentioned in previous part that NTFS suits computer best, and all partitions on this hard drive are NTFS partitions.
4K Sector Alignment
4K sector alignment might be strange to you, but it is quite important to large capacity hard drives, SSD, memory card, etc. Thus you may as well know a bit about it.
First, hard drive that is aligned to 4K sector works with fast speed; reduce wastage; extend lifespan; next, it means a lot to flash memory storage devices. Terminal based text editor.
This article is not going to introduce details of 4K sector alignment, for you can easily find many relevant materials online.
Free partition manager DiskGenius is able to check whether partitions on your computer align to 4K sectors, as picture below:
Suggestion: if your partition is not 4K sector aligned, then you can backup data and delete the partition to recreate a new one with DiskGenius which offers the option to align partition to 4K sectors. It is not advised to try those tools that claim they can make partition 4K sector aligned without data loss, because such kind of operation is very dangerous.
Other File System
As we all know, operating system runs on laptop or desktop doesn't restrict to Windows. Other operating system such as Mac and Linux are also very popular. Thus, there are many other file system types apart from FAT, NTFS and exFAT. If you have ever used Linux or Mac system, you'll know these file systems:
EXT: Ext is mainstream file system of Linux, including Ext2, Ext3 and Ext4.
HFS: Mac system mainly uses HFS and HFS+ file system.
This tutorial tells file system FAT, NTFS and exFAT and commonly used file system on Windows computer. Also 4K sector alignment is briefly touched upon. Next article will start actual partition operations to hard drive through DiskGenius.
| Filename extension | .hdf, .h4, .hdf4, .he2, .h5, .hdf5, .he5 |
|---|---|
| Magic number | 211HDFrn032n |
| Developed by | The HDF Group |
| Latest release | 5-1.10.7[1] (September 16, 2020; 3 months ago) |
| Type of format | Scientific data format |
| Open format? | Yes |
| Website | www.hdfgroup.org |
Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) is a set of file formats (HDF4, HDF5) designed to store and organize large amounts of data. Originally developed at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, it is supported by The HDF Group, a non-profit corporation whose mission is to ensure continued development of HDF5 technologies and the continued accessibility of data stored in HDF.
In keeping with this goal, the HDF libraries and associated tools are available under a liberal, BSD-like license for general use. HDF is supported by many commercial and non-commercial software platforms and programming languages. The freely available HDF distribution consists of the library, command-line utilities, test suite source, Java interface, and the Java-based HDF Viewer (HDFView).[2]
The current version, HDF5, differs significantly in design and API from the major legacy version HDF4.
Early history[edit]
The quest for a portable scientific data format, originally dubbed AEHOO (All Encompassing Hierarchical Object Oriented format) began in 1987 by the Graphics Foundations Task Force (GFTF) at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA). NSF grants received in 1990 and 1992 were important to the project. Around this time NASA investigated 15 different file formats for use in the Earth Observing System (EOS) project. After a two-year review process, HDF was selected as the standard data and information system.[3]
HDF4[edit]
HDF4 is the older version of the format, although still actively supported by The HDF Group. It supports a proliferation of different data models, including multidimensional arrays, raster images, and tables. Each defines a specific aggregate data type and provides an API for reading, writing, and organizing the data and metadata. New data models can be added by the HDF developers or users.
HDF is self-describing, allowing an application to interpret the structure and contents of a file with no outside information. One HDF file can hold a mix of related objects which can be accessed as a group or as individual objects. Users can create their own grouping structures called 'vgroups.'
The HDF4 format has many limitations.[4][5] It lacks a clear object model, which makes continued support and improvement difficult. Supporting many different interface styles (images, tables, arrays) leads to a complex API. Support for metadata depends on which interface is in use; SD (Scientific Dataset) objects support arbitrary named attributes, while other types only support predefined metadata. Perhaps most importantly, the use of 32-bit signed integers for addressing limits HDF4 files to a maximum of 2 GB, which is unacceptable in many modern scientific applications.
HDF5[edit]
The HDF5 format is designed to address some of the limitations of the HDF4 library, and to address current and anticipated requirements of modern systems and applications. In 2002 it won an R&D 100 Award.[6]
HDF5 simplifies the file structure to include only two major types of object:
- Datasets, which are multidimensional arrays of a homogeneous type
- Groups, which are container structures which can hold datasets and other groups
This results in a truly hierarchical, filesystem-like data format.[clarification needed][citation needed] In fact, resources in an HDF5 file can be accessed using the POSIX-like syntax /path/to/resource. Metadata is stored in the form of user-defined, named attributes attached to groups and datasets. More complex storage APIs representing images and tables can then be built up using datasets, groups and attributes.
In addition to these advances in the file format, HDF5 includes an improved type system, and dataspace objects which represent selections over dataset regions. The API is also object-oriented with respect to datasets, groups, attributes, types, dataspaces and property lists.
The latest version of NetCDF, version 4, is based on HDF5.
Because it uses B-trees to index table objects, HDF5 works well for time series data such as stock price series, network monitoring data, and 3D meteorological data. The bulk of the data goes into straightforward arrays (the table objects) that can be accessed much more quickly than the rows of an SQL database, but B-tree access is available for non-array data. The HDF5 data storage mechanism can be simpler and faster than an SQL star schema.[example needed]
Criticism[edit]
Hdd File Format For Mac And Pc Use
Criticism of HDF5 follows from its monolithic design and lengthy specification.
- HDF5 does not enforce the use of UTF-8, so client applications may be expecting ASCII in most places.
- Dataset data cannot be freed in a file without generating a file copy using an external tool (h5repack).[7]
Interfaces[edit]
Officially supported APIs[edit]
- CLI - .Net
- Fortran, Fortran 90
- HDF5 Lite (H5LT) – a light-weight interface for C
- HDF5 Image (H5IM) – a C interface for images or rasters
- HDF5 Table (H5TB) – a C interface for tables
- HDF5 Packet Table (H5PT) – interfaces for C and C++ to handle 'packet' data, accessed at high-speeds
- HDF5 Dimension Scale (H5DS) – allows dimension scales to be added to HDF5
Third-party bindings[edit]
- CGNS uses HDF5 as main storage
- Common Lisp library hdf5-cffi
- D offers bindings to the C API, with a high-level h5py style D wrapper under development
- Dymola introduced support for HDF5 export using an implementation called SDF (Scientific Data Format) with release Dymola 2016 FD01
- Erlang, Elixir, and LFE may use the bindings for BEAM languages
- Go - gonum's hdf5 package.
- HDFql enables users to manage HDF5 files through a high-level language (similar to SQL) in C, C++, Java, Python, C#, Fortran and R.
- Huygens Software uses HDF5 as primary storage format since version 3.5
- IGOR Pro offers full support of HDF5 files.
- JHDF5,[8] an alternative Java binding that takes a different approach from the official HDF5 Java binding which some users find simpler
- jHDF A pure Java implementation providing read-only access to HDF5 files
- JSON through hdf5-json.
- Julia provides HDF5 support through the HDF5 package.
- LabVIEW can gain HDF support through third-party libraries, such as h5labview and lvhdf5.
- Lua through the lua-hdf5 library.
- MATLAB, Scilab or Octave – use HDF5 as primary storage format in recent releases
- Mathematica[9] offers immediate analysis of HDF and HDF5 data
- Perl[10]
- Python supports HDF5 via h5py (both high- and low-level access to HDF5 abstractions) and via PyTables (a high-level interface with advanced indexing and database-like query capabilities). HDF4 is available via Python-HDF4 and/or PyHDF for both Python 2 and Python 3. The popular data manipulation package pandas can import from and export to HDF5 via PyTables.
- R offers support in the rhdf5 and hdf5r packages.
- Rust can gain HDF support through third-party libraries like hdf5.
Tools[edit]
- Apache Spark HDF5 Connector HDF5 Connector for Apache Spark
- Apache Drill HDF5 Plugin HDF5 Plugin for Apache Drill enables SQL Queries over HDF5 Files.
- HDF Product Designer Interoperable HDF5 data product creation GUI tool
- HDF Explorer A data visualization program that reads the HDF, HDF5 and netCDF data file formats
- HDFView A browser and editor for HDF files
- ViTables A browser and editor for HDF5 and PyTables files written in Python
See also[edit]
- Common Data Format (CDF)
- FITS, a data format used in astronomy
- GRIB (GRIdded Binary), a data format used in meteorology
- NetCDF, The Netcdf Java library reads HDF5, HDF4, HDF-EOS and other formats using pure Java
- Protocol Buffers - Google's data interchange format
References[edit]
- ^'HDF5 version 1.10.7 released on 2020-09-16'. Retrieved 16 Sep 2020.
- ^Java-based HDF Viewer (HDFView)
- ^'History of HDF Group'. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^How is HDF5 different from HDF4?Archived 2009-03-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^'Are there limitations to HDF4 files?'. Archived from the original on 2016-04-19. Retrieved 2009-03-29.
- ^R&D 100 Awards ArchivesArchived 2011-01-04 at the Wayback Machine
- ^Rossant, Cyrille. 'Moving away from HDF5'. cyrille.rossant.net. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^JHDF5 library
- ^HDF Import and Export Mathematica documentation
- ^PDL::IO::HDF5
External links[edit]
- Official website
This article is based on material taken from the Free On-line Dictionary of Computing prior to 1 November 2008 and incorporated under the 'relicensing' terms of the GFDL, version 1.3 or later.
